ECONOMICS
Chapter -2 Central Problem of an Economy
Ans. Economy problem arise due to the following three causes:-
(i) Unlimited Wants:- Human wants are unlimited no men can satisfy all his wants fully there for safely say that in every society at away given thing are enumerable unsatisfied wants.
(ii) Limited or scarce-mins:- Most of the goods and satisfying human wants are limited or scarce these goods are called scarce because their demand is grater then supply. No meter what is the prizes.
(iii) Alternatives uses:- The limited resources have alternative uses for Example:- Milk is a scare commodity. It can be used for cheese, Ice-cream, res-Gullah etc.
Since, resources are limited all wants can be satisfied so it lead to the problem of choice.
Central Problem:- Every Economy faces three central problems these are:-
(i) What to Produce.
(ii) How to Produce.
(iii) For Whom to Produce.
1. What to Produce:- These problem has two dimensions.
- What to Produce.
- How much to Produce.
Consumer Goods:- Sugar, Cloths, Wheat, Ghee.
Capital Goods:- Machines, cars, buses, tractors etc.
War time Goods:- Rifles, Guns, tanks etc.
Peace time Goods:- Bread or Butter.
2. How to Produce:- This is the second main problem of Economy this problem is concerned with the choice of technique of production and also concerned with the efficient use of resources. It implies more production at less cost.
- There are two techniques of production:-
(i) Labour intensive Technique (LIT) Under this technique, labour is used more then capital.
(ii) Capital intensive technique:- Under this technique capital is used more then labour.
- Technique is to be used in a given industry's so that productivity raised and cost is lowered.
P.P.C (Production Possibility Curve)
It is a curve showing different combination of two goods which can be produced with available and technique of production.
- This curve is also called transformation curve because it indicates that if more of good-x is to be produce then the production will have to be withdrawn an from the production on of y and transformation to the production of good-x.
- In P.P.C technology, given resources remains constant.
Attendable:-Any point on the boundary line of production is a point that shows attendable combination of output of two goods.
Unattendable:- Any point outside the boundary line of production shows unattendable combination of two goods.
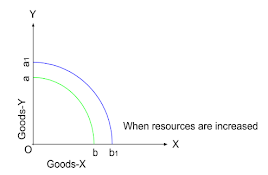
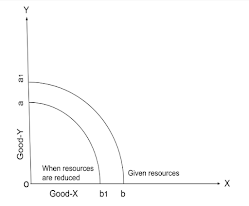
Sifting/Rotation of P.P.C
It will shift under the following condition.
- Change in Resources:-
and P.P.C shift to the right.
- Change in Technology:-
It means grater production of both good-X and good-y with the same resources there for P.P.C would shift to the right from ab to a1b1.
Basic properties of P.P.C:- There are two properties of P.P.C.
(i) P.P.C slopes downward:-
(ii) P.P.C is concave to the point of origin:-
P.P.C slopes downwards from left to right because is a situation of fuller utilization of the given resources, production of both the goods can not be produced only with the less of good-Y.
P.P.C is concave to the point of origin because to produce each additional unit of good-X, More and more units of good-Y will have to sacrificed then before.
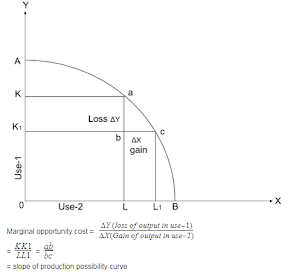
Opportunity cost:- It refers to value of factor in it next best alternative use.
Marginal opportunity cost:- It is the rate at which output of good-Y is to be sacrificed for additional units of good-X. Therefor it refers to the slope of P.P.C.
★ Using the concept of P.P.C, We can explain central Problems of an economy.
- What to Produce:-
Example:- P.P.C sows all the resources are used in the production of good-X you can produced 6 tonnes of wheat corresponding to point 'D'.On the other hand, if all the resources used in the production of good-Y(clothes) you can produced 12 boles of clothes corresponding to point 'A'.
Any point on the P.P.C correspond to full utilization of resources thus, Point 'B' shows the production of 2 tones wheat and 10 bales of clothes. Point 'C' shows the production of 4 tones wheat and 6 bales of clothes.
Q.1. If the production of one commodity is increased then production of the other has to be decreases why?
Ans. It is because the given resources limited and fully utilized, therefore the problem of allocation of resources across their arise.
- How to Produced:-
- For Whom to Produce:-
Fuller utilization of resources:- Any point on the curve P.P.C AD(Like a point P) corresponds to fuller as well as efficient utilization of resources.
- It shows the potential level of output.
- Potential level of output refers to the maximum output which can be produced the given resources and technology.




















0 Comments